is atp a carbohydrate 24.2 carbohydrate metabolism – anatomy & physiology
Do you ever wonder how your body prefers to use certain nutrients? Well, I found some interesting information that sheds light on this topic! Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of carbohydrate metabolism.
Carbohydrate Metabolism Explained
Carbohydrate metabolism is a complex process that involves the breakdown and utilization of carbohydrates in our body. It plays a crucial role in providing energy to fuel various bodily functions. While carbohydrates may have received a bad reputation in recent years, our bodies actually favor the use of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from carbohydrates over lipids (fats).
 ATP: The Energy Currency
ATP: The Energy Currency
ATP is often referred to as the “energy currency” of our body. It is a molecule that stores and transports energy within cells. When carbohydrates are digested, they are broken down into glucose molecules. These glucose molecules then enter our cells, where they are further metabolized to produce ATP.
Why does our body prefer to use ATP derived from carbohydrates over lipids? It’s because carbohydrate metabolism is a more efficient and rapid process compared to lipid metabolism. Carbohydrates can be readily converted into ATP, providing quick bursts of energy when needed.
 The Role of Insulin
The Role of Insulin
Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, plays a vital role in carbohydrate metabolism. When we consume carbohydrates, our blood glucose levels rise. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, which helps transport glucose into cells for energy production or storage.
Insulin also regulates the balance between carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. When insulin levels are high, our body tends to preferentially use carbohydrates for energy. On the other hand, when insulin levels are low, such as during fasting or certain dietary conditions, our body switches to using stored lipids for energy production.
A Balanced Approach
While our body favors the use of ATP derived from carbohydrates, it doesn’t mean that we should solely rely on carbs for our energy needs. A balanced approach is key. Our body can efficiently utilize a combination of carbohydrates, lipids, and even proteins for energy production.
It’s important to note that the type and quality of carbohydrates we consume also matter. Opting for complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provides a slow and steady release of glucose into our bloodstream. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and provides a sustained source of energy.
So, the next time you reach for a snack or plan your meals, keep in mind the fascinating world of carbohydrate metabolism. Our body’s preference for ATP derived from carbohydrates helps us understand the importance of a balanced diet and the role of different nutrients in fueling our daily activities.
If you are searching about 24.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism – Anatomy & Physiology you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pictures about 24.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism – Anatomy & Physiology like 24.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism – Anatomy & Physiology, Is Atp A Carbohydrate Lipid Or Protein - Wasfa Blog and also ATP Yield of Carbohydrate Catabolism - YouTube. Here it is:
24.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism – Anatomy & Physiology
 open.oregonstate.educationmetabolism carbohydrate digestion transport electron chain respiration anatomy physiology cellular energy cycle glycolysis krebs cell produced stages figure involves carbohydrates
open.oregonstate.educationmetabolism carbohydrate digestion transport electron chain respiration anatomy physiology cellular energy cycle glycolysis krebs cell produced stages figure involves carbohydrates
Is Atp A Carbohydrate Lipid Or Protein - Wasfa Blog
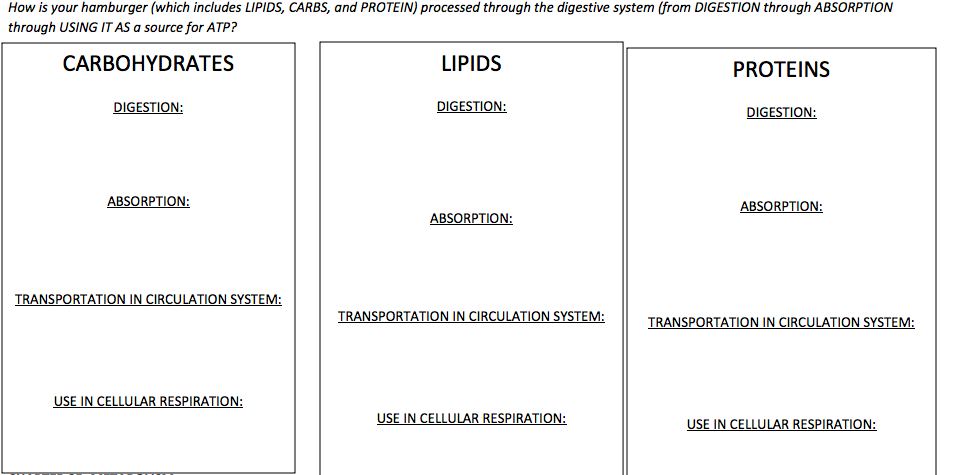 wasfa-hd.blogspot.comatp carbohydrate lipid lipids solved
wasfa-hd.blogspot.comatp carbohydrate lipid lipids solved
Atp Yield From Carbohydrate Fat And Protein Metabolism - Wasfa Blog
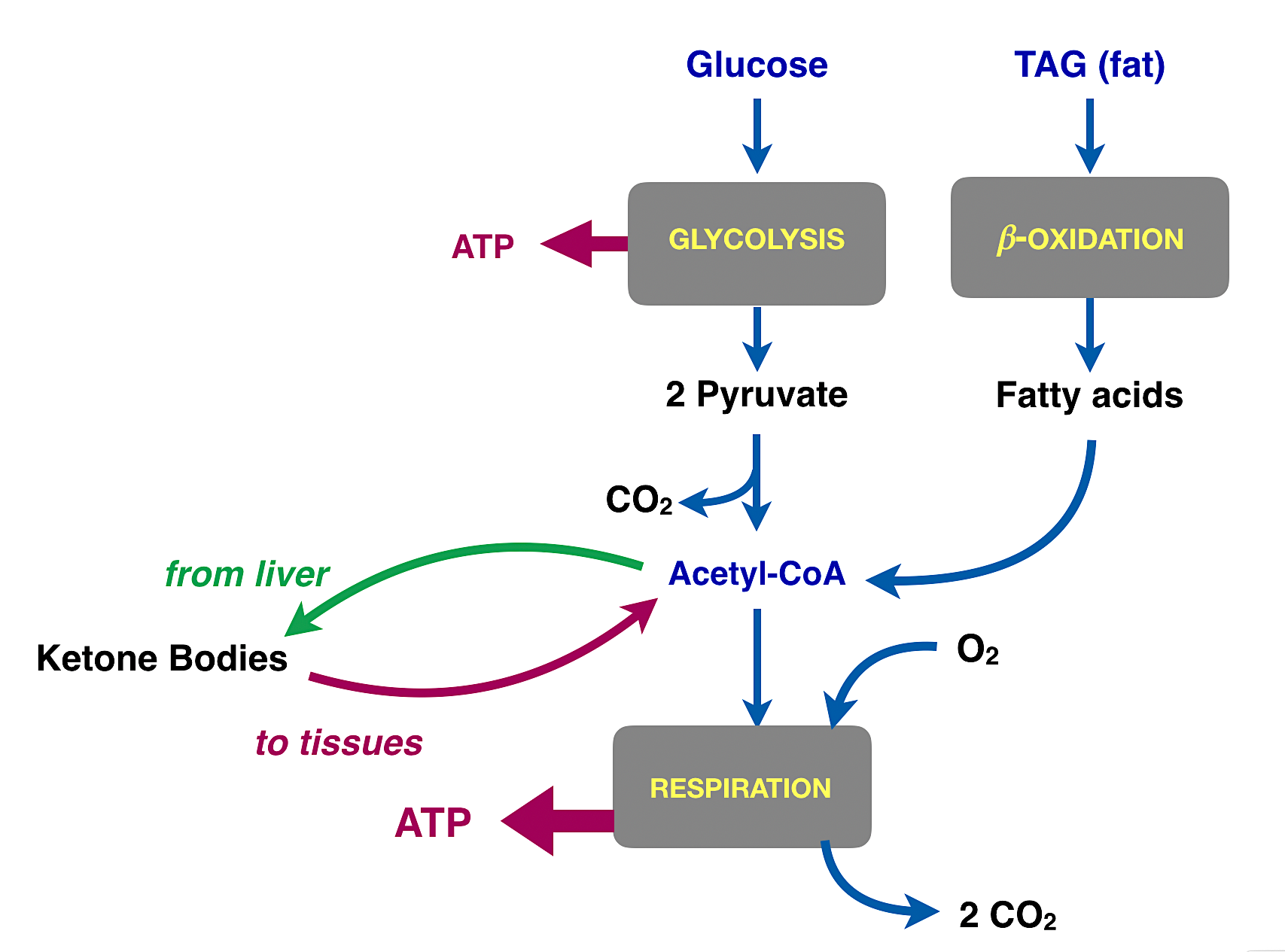 wasfa-hd.blogspot.commetabolism atp carbohydrate yield crossfit glycolysis metabolic respiration
wasfa-hd.blogspot.commetabolism atp carbohydrate yield crossfit glycolysis metabolic respiration
ATP Yield Of Carbohydrate Catabolism - YouTube
 www.youtube.comBody Favors The Use Of ATP Carbohydrate Rather Than Lipids.docx - Body
www.youtube.comBody Favors The Use Of ATP Carbohydrate Rather Than Lipids.docx - Body
 www.coursehero.comMetabolism atp carbohydrate yield crossfit glycolysis metabolic respiration. Atp yield of carbohydrate catabolism. Metabolism carbohydrate digestion transport electron chain respiration anatomy physiology cellular energy cycle glycolysis krebs cell produced stages figure involves carbohydrates
www.coursehero.comMetabolism atp carbohydrate yield crossfit glycolysis metabolic respiration. Atp yield of carbohydrate catabolism. Metabolism carbohydrate digestion transport electron chain respiration anatomy physiology cellular energy cycle glycolysis krebs cell produced stages figure involves carbohydrates